Contents
Pig Kidney Transplants has long been hampered by the scarcity of suitable donor organs, leading to lengthy waiting lists and a pressing need for alternative solutions. In recent years, xenotransplantation—the transplantation of organs or tissues between different species—has emerged as a potential solution to address this critical shortage. Among the most promising candidates for xenotransplantation are pig kidneys, offering hope for patients in need of life-saving organ transplants. In this article, we’ll explore the science behind pig kidney transplants, the challenges they present, and the potential they hold for revolutionizing the field of organ transplantation.
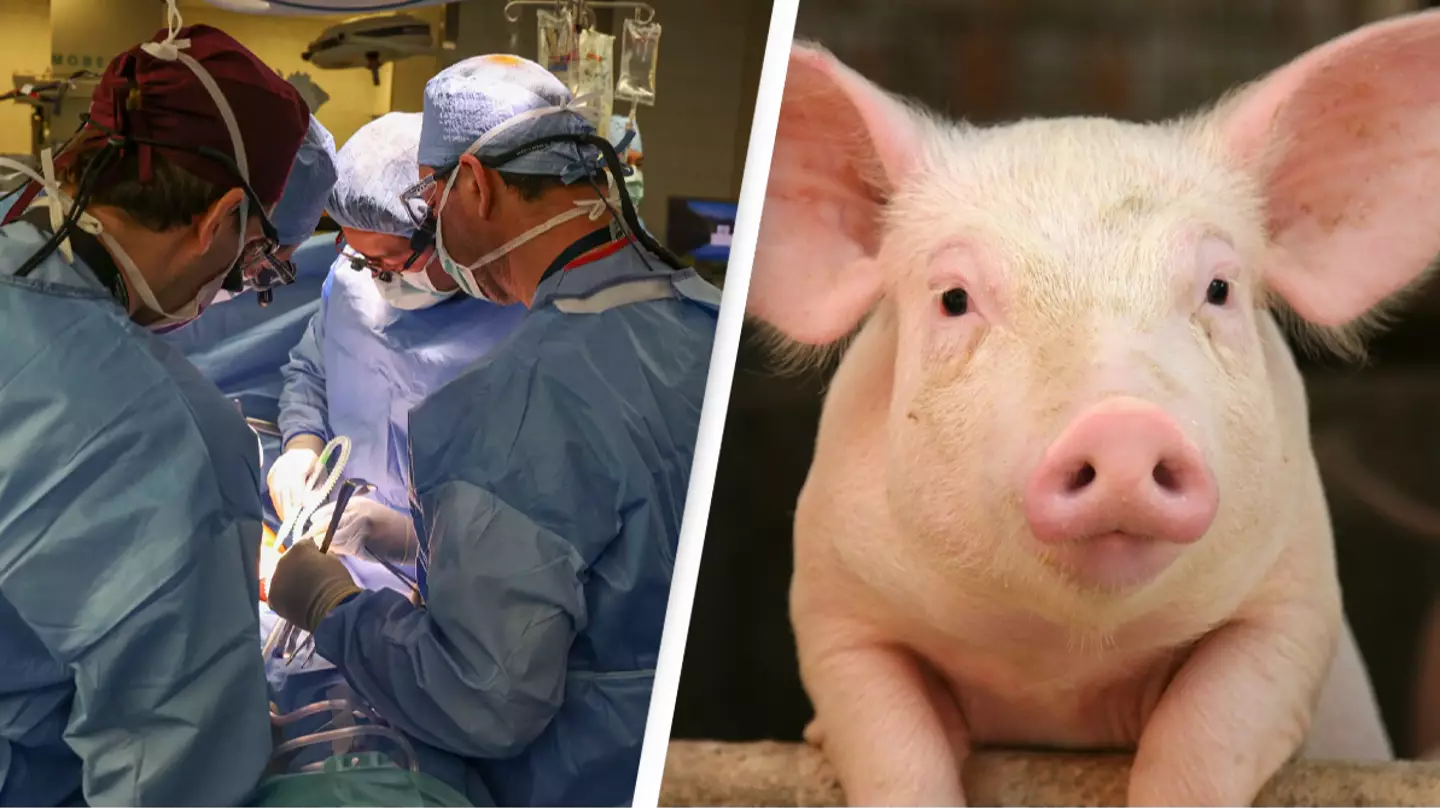

The Need for Alternative Solutions
Organ transplantation is often the only viable treatment option for patients with end-stage organ failure. However, the demand for donor organs far exceeds the available supply, leading to significant waiting times and a high risk of mortality for patients on transplant waiting lists. Xenotransplantation offers a potential solution to this critical shortage by harnessing organs from non-human species, such as pigs, to supplement the donor pool and provide lifesaving transplants to those in need.
Why Pig Kidneys?
Pigs are considered ideal candidates for xenotransplantation for several reasons. Firstly, their organs are anatomically and physiologically similar to human organs, making them compatible for transplantation. Additionally, pigs are readily available, have large litter sizes, and reach maturity relatively quickly, making them a practical and sustainable source jpslot of donor organs. Pig kidneys, in particular, have shown promise due to their similar size and function to human kidneys, offering the potential for successful transplantation and long-term graft survival.
Overcoming Immunological Barriers
One of the primary challenges in xenotransplantation is the risk of rejection—the recipient’s immune system may recognize the transplanted organ as foreign and mount an immune response, leading to organ failure. To address this challenge, researchers have developed innovative techniques to modify pig organs and minimize the risk of rejection. This includes genetic engineering to remove antigens that trigger immune responses, as well as immune-modulating drugs to suppress the recipient’s immune system and promote tolerance to the transplanted organ.
Ethical and Regulatory Considerations
While pig kidney transplants offer immense potential, they also raise ethical and regulatory considerations that must be carefully addressed. Concerns include animal welfare, the risk of transmitting infectious diseases from pigs to humans (known as zoonotic diseases), and the potential for genetic modification to alter the integrity of the pig genome. Ethical frameworks, regulatory guidelines, and rigorous oversight are essential to ensure that pig kidney transplants proceed ethically, safely, and responsibly.
The Future of Pig Kidney Transplants
Despite the challenges and uncertainties, pig kidney transplants represent a promising frontier in organ transplantation, offering hope for patients facing organ failure and transforming the landscape of medical treatment. Ongoing research efforts continue to advance the science of xenotransplantation, with the ultimate goal of developing safe, effective, and widely accessible pig kidney transplants for patients around the world. By addressing the technical, ethical, and regulatory challenges associated with pig kidney transplants, we can unlock their full potential and usher in a new era of organ transplantation.
Exploring the Pros and Cons of Pig Kidney Transplants
Pig kidney transplants, a form of xenotransplantation, hold promise as a potential solution to address the critical shortage of donor organs for patients with end-stage renal disease. However, like any medical procedure, pig kidney transplants come with their own set of advantages and disadvantages. In this article, we’ll delve into the pros and cons of pig kidney transplants, highlighting both their potential benefits and challenges.
/arc-anglerfish-arc2-prod-pmn.s3.amazonaws.com/public/DCGORXVQ7JC3LM3QHHOH6DTMUY.jpg)
Advantages of Pig Kidney Transplants:
- Expanded Donor Pool: Pig kidney transplants have the potential to significantly expand the pool of available organs for transplantation, reducing waiting times and improving access to life-saving treatment for patients with end-stage renal disease.
- Anatomical and Physiological Similarity: Pig kidneys share anatomical and physiological similarities with human kidneys, making them compatible for transplantation and reducing the risk of rejection compared to organs from other species.
- Readily Available Supply: Pigs are readily available, have large litter sizes, and reach maturity relatively quickly, making them a practical and sustainable source of donor organs for transplantation.
- Potential for Genetic Modification: Advances in genetic engineering technologies allow for the modification of pig organs to minimize the risk of rejection and improve compatibility with the human immune system, increasing the likelihood of successful transplantation.
Disadvantages of Pig Kidney Transplants:
- Risk of Rejection: Despite efforts to minimize the risk of rejection, pig kidney transplants still carry the risk of immune-mediated rejection, wherein the recipient’s immune system recognizes the transplanted organ as foreign and mounts an immune response.
- Zoonotic Disease Transmission: There is a potential risk of transmitting infectious diseases from pigs to humans (zoonotic diseases) through pig kidney transplants. Strict screening protocols and surveillance measures are necessary to mitigate this risk and ensure patient safety.
- Ethical Considerations: Pig kidney transplants raise ethical considerations related to animal welfare, genetic modification, and the use of animals for medical purposes. Ethical frameworks and regulatory guidelines are needed to ensure that pig kidney transplants proceed ethically and responsibly.
- Long-term Outcomes: Long-term outcomes and survival rates of pig kidney transplants are still being evaluated, and more research is needed to assess the durability and efficacy of these transplants over time.
Conclusion:
Pig kidney transplants offer potential benefits in expanding the donor pool and improving access to life-saving treatment for patients with end-stage renal disease. However, they also present challenges related to immune rejection, disease transmission, ethical considerations, and long-term outcomes. Continued research, innovation, and regulatory oversight are essential to address these challenges and maximize the potential of pig kidney transplants as a viable option for organ transplantation.
Understanding the Process of Pig Kidney Transplants
Pig kidney transplants, a form of xenotransplantation, offer a potential solution to the critical shortage of donor organs for patients with end-stage renal disease. While the process involves complexities and challenges, advancements in medical science have made pig kidney transplants a viable option for some patients. In this article, we’ll explore the steps involved in pig kidney transplants, from donor selection to post-transplant care.

1. Donor Selection:
The first step in the process of pig kidney transplants is the selection of suitable donor pigs. Donor pigs are carefully screened for health, genetic compatibility, and absence of infectious diseases that could pose risks to the recipient. Pigs selected for organ donation are typically raised in controlled environments to minimize exposure to pathogens and ensure optimal health.
2. Genetic Modification:
To minimize the risk of rejection and improve compatibility with the human immune system, donor pigs may undergo genetic modification. This involves the introduction of specific genetic alterations to reduce the expression of antigens that trigger immune responses in humans. Genetic engineering technologies such as CRISPR-Cas9 allow for precise modifications to the pig genome, enhancing the viability of pig organs for transplantation.
3. Organ Harvesting:
Once a suitable donor pig is identified and genetically modified, the next step is to harvest the pig kidney for transplantation. The surgical procedure involves carefully removing the kidney from the donor pig while maintaining organ viability and minimizing tissue damage. Preservation techniques such as cold perfusion may be employed to protect the kidney during transport to the transplant facility.
4. Recipient Preparation:
Before undergoing pig kidney transplantation, recipients undergo thorough medical evaluation and preparation. This includes assessments of overall health, kidney function, and immunological compatibility. Recipients may undergo pre-transplant testing, including blood tests, imaging studies, and tissue typing, to ensure compatibility with the donor organ and minimize the risk of rejection.
5. Surgical Procedure:
The transplant surgery itself involves the implantation of the pig kidney into the recipient’s body. Surgeons carefully connect the blood vessels and ureter of the pig kidney to the recipient’s circulatory and urinary systems, ensuring proper blood flow and drainage. The surgical procedure may take several hours to complete and requires meticulous attention to detail to ensure successful transplantation.
6. Post-Transplant Care:
Following pig kidney transplantation, recipients require intensive post-operative care to monitor graft function, prevent complications, and manage immunosuppressive therapy. Immunosuppressive medications are prescribed to suppress the recipient’s immune system and prevent rejection of the transplanted organ. Recipients undergo regular follow-up appointments, blood tests, and imaging studies to assess graft function and adjust medication regimens as needed.
Conclusion:
Pig kidney transplants represent a complex yet promising approach to addressing the shortage of donor organs for patients with end-stage renal disease. By leveraging advancements in genetics, surgery, and immunology, researchers and clinicians continue to refine the process of pig kidney transplantation, improving outcomes and expanding access to life-saving treatment for patients in need. With ongoing research and innovation, pig kidney transplants hold the potential to revolutionize the field of organ transplantation and offer hope to countless individuals awaiting a second chance at life.
Read More Article About “BEETLEJUICE BEETLEJUICE’: THE AWAITED SEQUEL CONJURES NOSTALGIA AND NEW SCARES“